Introduction
Core Transit can provide static IP addresses and internet termination services in various situations where a static IP address is otherwise unavailable. The Ethernet Anywhere static IP architecture includes use cases such as mobile locations, locations with no wired connectivity options, or cases where a backup LTE wireless connection is desired. The static IP addresses can also be made available behind service provider carrier-grade NAT (network address translation) gateways or on networks where IP address allocation is dynamic.
Technical Summary
To deliver these services Ethernet Anywhere Edge Lite device builds a tunnel to the Core Transit network. A tunnel is simply data encapsulated and routed over an underlying network in network connectivity. In the diagram below the Edge Lite device on the left builds this tunnel over the underlying network back to a preselected Core Transit data center. In addition to LTE, satellite and broadband internet connections can also serve as redundant paths to Core Transit when needed.
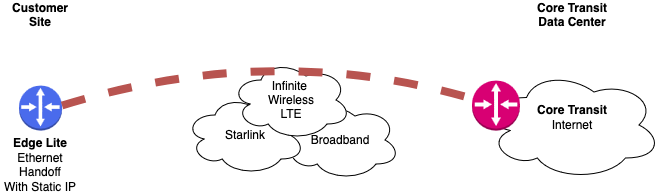
Getting Connected
With an Ethernet Anywhere Edge Lite in place, provisioning a static IP address is easy. Simply plug your router or firewall directly into the designated port on the back of the Edge Lite. This interface will present the connection as if an ethernet cable has been stretched between the Core Transit network directly to your device. With an active link, you can then configure your device with the static IP address information provided by Core Transit.
IP Addressing Designs
The default configuration is a simple point-to-point ethernet link leveraging the RFC 3021 IPv4 /31 addressing configuration. This allows Core Transit to keep addressing as efficent. If you device does not support this configuration optional /30 and larger IPv4 address blocks are also available.
WAN Address Block Design
The Core Transit standard addressing design is to implement addresses on the link between Core Transit and the end customer end device. This is simple yet flexible suiting most applications. Address block size can be adjusted when you order to further add flexibility to the configuration as needed. The default configuration is an IPv4 /31. A /30, /29, or larger block is also an option if your device does not support this configuration or if you need to address multiple devices directly. In this case, all publicly addressed interfaces will leverage the IP address on Core Transit’s side of the link as their default gateway or default route. In the digram below a switch is used to break out this connection to service more endpoints.
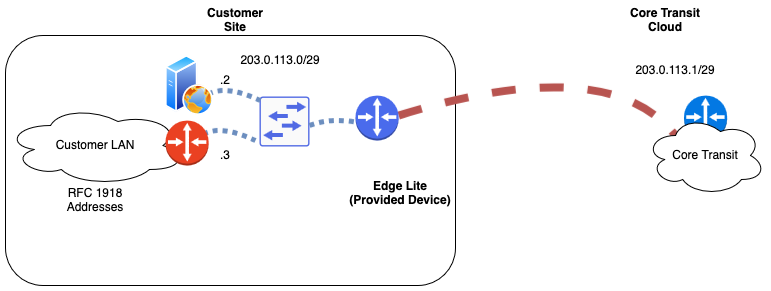
Route IP Block Design
An alternative design would be to leverage the point-to-point link between Core Transit and the customer router strictly as a point-to-point WAN link with an address block routed down the link by Core Transit. This design permits additional flexibility and allows the administrator to use this address block with more flexibility for NAT, or to route deeper into the customer network.
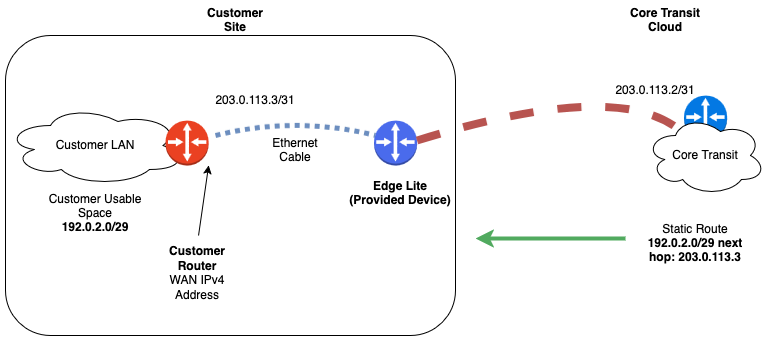
IPv4 Address Allocation
With the default link allocation being a /31 this means there can only ever be two IPv4 addresses in the total allocation. The first address in the subnet is always the Core Transit side of the link and the second will be the customer assignable address.
This address can be assigned statically. This is often desired as the administrator can produce a device configuration with finite values already defined. In addition to a static address Core Transit will also dynamically assign addresses to customer devices via DHCP. Of course in the case of a /31 only a single address is available to be assigned. This option allows for quick connectivity for the customer. Additionally, if a customer desires the ability to manually move a firewall our routing device from one internet connection to another at will, this can also come in handy. DHCP assignment of “static” addresses can greatly reduce the need for truck rolls and other site visit activity.
IPv6 Address Allocation
For IPv6 address allocation there will be a statically assigned /64 on the link between Core Transit and the customer device. The first address in the /64 will be the Core Transit router IP address. Additional IPv6 addresses on the link can be dynamically assigned or hard coded with a static route toward the Core Transit address.
A customer-usable IPv6 allocation is then available via prefix delegation for assignment deeper into the network. This is typically a /60 which is will often suffice for most small site use cases. If you need a larger allocation they are available as a nominal cost addon in the client portal.